Understanding TV Power Consumption
The power consumption of a TV is typically measured in watts (W) and can vary significantly based on several factors:
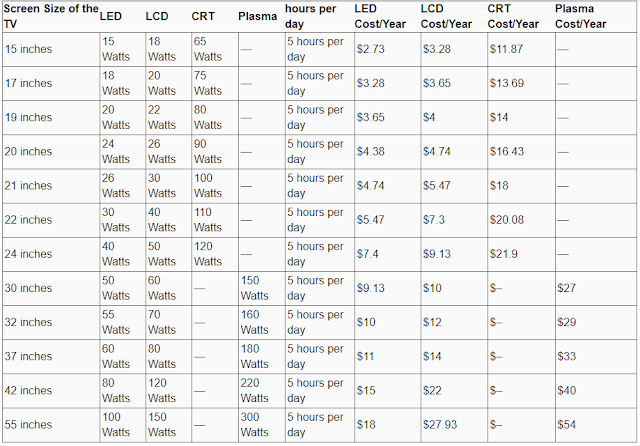
Average Power Consumption by TV Type
Calculating Annual Energy Usage
To estimate the annual energy usage of your TV, you can use the following formula:
Annual Energy Usage (in kilowatt-hours, kWh) = Power Consumption (in watts) x Hours of Daily Use x 365 days / 1000
For example, if you have a 55-inch LED TV that consumes 100 watts and you use it for 4 hours a day, the annual energy usage would be:
Annual Energy Usage = 100 watts x 4 hours x 365 days / 1000 = 146 kWh
Tips for Reducing TV Energy Usage
In conclusion, the power consumption of LCD and LED TVs varies by size, type, and usage. While larger screens and higher brightness settings generally consume more power, modern LED TVs are designed to be energy-efficient. By adjusting settings and practicing energy-conscious habits, you can reduce your TV's energy usage and lower your electricity bills while enjoying your favorite shows and movies.
Tv Power Consumption Chart
@Assumes electricity cost per unit .10c
Factors that affecting power consumption of Tv
The power consumption of a TV can be influenced by various factors, and understanding these factors can help you manage and optimize your TV's energy usage. Here are the key factors that affect the power consumption of a TV:
1. Screen Size: Larger TVs typically consume more power than smaller ones because they require larger backlighting systems to maintain consistent brightness. The difference in power consumption becomes more pronounced as you move to much larger screen sizes.
2. Display Technology: The type of display technology used in the TV plays a significant role. Common types include LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), LED (Light Emitting Diode), OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), and QLED (Quantum Dot LED). Among these, OLED and QLED tend to be more energy-efficient because they can individually control each pixel's brightness.
3. Brightness and Contrast: Higher brightness and contrast settings require more power. Reducing these settings can significantly reduce energy consumption without sacrificing picture quality.
4. Content and Usage: The type of content you watch and how you use your TV affects power consumption. Streaming videos or playing video games, especially those with intense graphics, can use more power than displaying static images or text.
5. Energy-Saving Features: Many modern TVs come equipped with energy-saving features and modes. Activating these modes can reduce power consumption by adjusting settings like brightness, backlight, and screen timeout when the TV is idle.
6. Picture Mode: TVs often have preset picture modes like "Cinema," "Game," or "Standard." Some of these modes are optimized for energy efficiency. Choosing the right mode for your content can help conserve energy.
7. Screen Resolution: TVs with higher resolutions (e.g., 4K) may consume slightly more power than those with lower resolutions (e.g., 1080p). However, the impact on power consumption is generally not as significant as other factors.
8. Age and Technology: Older TVs may use older, less energy-efficient technologies, which can result in higher power consumption. Newer models are typically designed with energy efficiency in mind.
9. Standby Power: Many TVs consume power even when they are turned off, thanks to standby modes. While the power draw in standby mode is usually low, it can accumulate over time. Using a power strip or unplugging the TV when not in use can eliminate this standby power consumption.
10. Ambient Light: The amount of ambient light in your viewing environment can affect how you perceive the TV's brightness. In a bright room, you might turn up the TV's brightness, increasing power consumption.
11. Smart Features: Smart TVs, which can connect to the internet and run apps, may consume more power when actively using these features. Disabling Wi-Fi or using energy-saving settings can help reduce power consumption.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your TV's usage and settings to minimize power consumption while enjoying your favorite content. Additionally, checking the TV's energy label, such as ENERGY STAR certification, can help you identify models that meet specific energy efficiency guidelines.