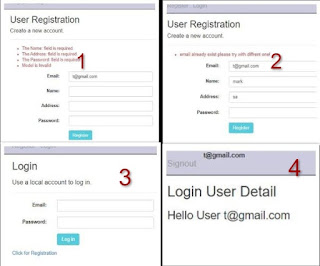
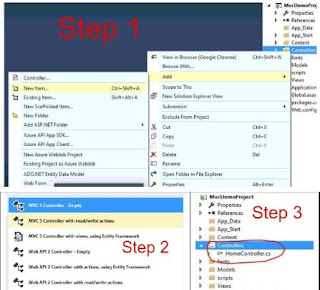
In the last asp.net article, we have discussed how to create custom login and registration in asp net MVC 5 without entity framework.
In this ASP.NET post, we will learn how to create a complete custom login, logout, and registration system using Entity Framework with jQuery validation in MVC with authentication.
We will implement the login and registration functionality with the assistance of Entity Framework, proceeding step by step to understand the entire system. This article is particularly beneficial for beginners in ASP.NET MVC who wish to learn the optimal approach for user registration and login, as commonly used in real-world projects.
Our objective is to develop a basic login and registration page where users can log in and register for an account.
MVC Pattern
A Dynamic Website is a website whose content changes based on user input. It typically follows a 3-tier architecture, consisting of three main parts. In contemporary software development, this architecture is often referred to as the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern.
MVC is a software design pattern widely regarded as one of the best. It facilitates the design, development, debugging, management, maintenance, updating, upgrading, and extension of various types of software.
This pattern essentially comprises three components, which correspond to the three tiers of the 3-Tier Architecture: the Client Tier, which represents the View part of the MVC Pattern; the Middle Tier, which represents the Controller part of the MVC Pattern; and the Server Tier, which represents the Model part of the MVC Pattern. Consequently, the 3-Tier Architecture is characterized by the Model, View, and Controller parts of the MVC pattern.
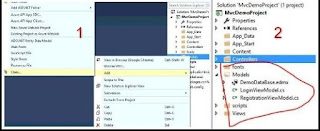
Let's begin by creating a table named Users to store user data.
Sql Script:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Company_Users](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](max) NOT NULL,
[Email] [nvarchar](max) NOT NULL,
[Address] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
[Encryptedpassword] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_TblUsers] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
LoginViewModel Class
public class LoginViewModel
{
[Required]
[EmailAddress]
[Display(Name = "Email: ")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Password: ")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}RegistrationViewModel Class
public class RegistrationViewModel
{
[Required]
[Display(Name = "Name: ")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[EmailAddress]
[StringLength(150)]
[Display(Name = "Email: ")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name = "Address: ")]
public string Address { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[StringLength(150, MinimumLength = 6)]
[Display(Name = "Password: ")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
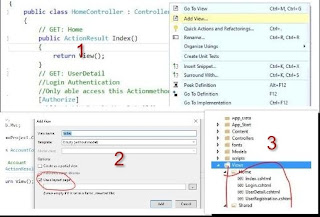
Step 4-Create ActionResult for login and registration in HomeController
using MvcDemoProject.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Security;
namespace MvcDemoProject.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
// GET: Home
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
// GET: UserDetail
//Login Authentication
//Only able access this Actionmethod when User Log in
[Authorize]
public ActionResult UserDetail()
{
return View();
}
// GET:Login
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
//Post:Login
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Login(LoginViewModel LoginViewModel)
{
if (IsAuthenitcatedUser(LoginViewModel.Email, LoginViewModel.Password))
{
//MVC and Login Authentication
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(LoginViewModel.Email, false);
return RedirectToAction("UserDetail", "Home");
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Your credentail is incorrect");
}
return View(LoginViewModel);
}
// GET:Register return view
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult UserRegistration()
{
return View();
}
// Post:Register
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult UserRegistration(RegistrationViewModel RegistrationViewModel)
{
try
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
if (!IsEmailExist(RegistrationViewModel.Email))
{
using (DemoDataBaseEntities db = new DemoDataBaseEntities())
{
Company_Users userobj = new Company_Users
{
Email = RegistrationViewModel.Email,
Name = RegistrationViewModel.Name,
//for encryption you should use a strong and secure Algorithm
// I'm simply using Base64 for explanation purpose
Encryptedpassword = Base64Encode(RegistrationViewModel.Password),
Address = RegistrationViewModel.Address
};
db.Company_Users.Add(userobj);
if (db.SaveChanges()>0)
{
//Set MVC and Login Authentication
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(RegistrationViewModel.Email, false);
return RedirectToAction("UserDetail", "Home");
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Something went wrong please try again later!");
}
}
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "email already exist please try with diffrent one!");
}
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Model is Invalid");
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", e.Message);
}
return View();
}
public ActionResult SignOut()
{
FormsAuthentication.SignOut();
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
private bool IsEmailExist(string email)
{
bool IsEmailExist = false;
using (DemoDataBaseEntities db = new DemoDataBaseEntities())
{
int count = db.Company_Users.Where(a => a.Email == email).Count();
if (count > 0)
{
IsEmailExist = true;
}
}
return IsEmailExist;
}
private bool IsAuthenitcatedUser(string email, string password)
{
var encryptpassowrd = Base64Encode(password);
bool IsValid = false;
using (DemoDataBaseEntities db = new DemoDataBaseEntities())
{
int count = db.Company_Users.Where(a => a.Email == email && a.Encryptedpassword == encryptpassowrd).Count();
if (count > 0)
{
IsValid = true;
}
}
return IsValid;
}
private static string Base64Encode(string PlainPassword)
{
var plainTextBytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(PlainPassword);
return System.Convert.ToBase64String(plainTextBytes);
}
}
}The HomeController class represents the controller responsible for managing user interactions within the application.
- Index Action Method: This method handles the request for the home page and returns the corresponding view.
UserDetail Action Method: This method is decorated with the [Authorize] attribute, ensuring that only authenticated users can access it. It returns the view for displaying user details.
Login Action Methods:
- The Login method handles GET requests and returns the view for user login.
- The Login method decorated with [HttpPost] and [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] attributes handles POST requests for user login. It validates the provided credentials against the database. If the credentials are valid, it sets an authentication cookie and redirects the user to the UserDetail action method. If not, it adds a model error to the view.
UserRegistration Action Methods:
- The UserRegistration method handles GET requests and returns the view for user registration.
- The UserRegistration method decorated with [HttpPost] and [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] attributes handles POST requests for user registration. It validates the provided registration data, checks if the email already exists in the database, encrypts the password, and saves the user data to the database. If successful, it sets an authentication cookie and redirects the user to the UserDetail action method.
SignOut Action Method:
- This method signs out the current user by clearing the authentication cookie and redirects them to the home page.
Helper Methods:
- IsEmailExist: Checks if the provided email already exists in the database.
- IsAuthenticatedUser: Validates the user's credentials against the database.
- Base64Encode: Encodes the password using Base64 encoding for storage in the database.
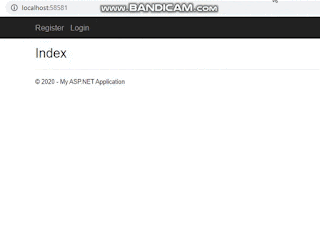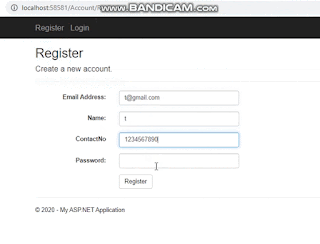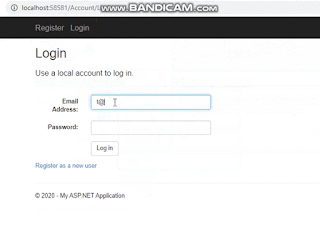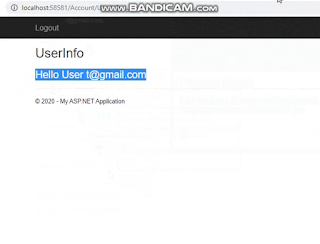
Index.cshtml
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>Welcome to Login and Registration Portal</h2>
UserDetail.cshtml
@{
ViewBag.Title = "UserDetail";
}
<h2>Login User Detail</h2>
<h3>Hello User @HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name </h3>Login.cshtml
@model MvcDemoProject.Models.LoginViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Login";
}
<h2>Login</h2>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8">
<section id="loginForm">
@using (Html.BeginForm("Login", "Home", new { ReturnUrl = ViewBag.ReturnUrl }, FormMethod.Post, new { @class = "form-horizontal", role = "form" }))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<h4>Use a local account to log in.</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Email, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Email, new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Email, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Password, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password, new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Password, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<button class="btn btn-info" type="submit">Log in</button>
</div>
</div>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Click for Registration", "Register")
</p>
}
</section>
</div>
</div>UserRegistration.cshtml
@model MvcDemoProject.Models.RegistrationViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Register";
}
<h2>User Registration</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm("UserRegistration", "Home", FormMethod.Post, new { @class = "form-horizontal", role = "form" }))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<h4>Create a new account.</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary("", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Email, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Email, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Name, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Name, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Address, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(m => m.Password, new { @class = "col-md-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<button class="btn btn-info" type="submit">Register</button>
</div>
</div>
}
<system.web>
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms loginUrl="/Home/Login" timeout="20"></forms>
</authentication>
</system.web>DownLoad Source Code
- <forms>: This element configures forms authentication settings.
- loginUrl="/Home/Login": Specifies the URL to redirect to for user authentication if they are not already authenticated. In this case, if a user attempts to access a protected resource without being authenticated, they will be redirected to the /Home/Login page to log in.
- timeout="20": Specifies the timeout duration for the authentication cookie in minutes. After 20 minutes of inactivity, the user's authentication session will expire, and they will need to log in again.
This configuration ensures that forms authentication is enabled, specifies the login URL, and sets a timeout for authentication sessions.
Advantages of MVC / Why is MVC used?
- With the help of MVC, you can get both the view part and the logic part i.e. designer and developer to work on a project simultaneously.
- With this, you can group the related action/method of logic together and group the view and its specific model together. So that you can complete your project in a short time.
- The code becomes easier to manage.
- From one model you can attach with multiple view parts. In the MVC based prokect, you get ease in doing code modification.
MVC History
Read Similar Articles
- Instead Of Delete Trigger In Sql Server With Example
- Pivot Rows to columns In Sql Server
- Replacing NULL and Empty string in Select statement
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Indexes In Sql Server?
- How to Display Binary Image in Gridview from Database in Asp .Net c#
- How To Change Database Table Columns Without Dropping The Table